Our Modules
These are examples of the kinds of modules that we bring on our school visits and to events.
Comparative Neuroanatomy
Recommended audience: all ages and grades
An interactive demonstration of comparative neuroanatomy with the brains of several different species, including human.
“Ask a Neuroscientist” Panel
Recommended audience: all ages and grades
Ask a Neuroscience graduate student on various topics related to education, science research, and what a day is like in the life of a budding neuroscientist!
Artificial Neural Networks
Recommended audience: middle school and above
Build and train an artificial neural network to recognize hand-written numbers. Students can draw their own numbers over Zoom and experiment with the limits of the network.
Statistical Data Analysis
Recommended audience: middle school and above
An introductory lesson to data collection and statistical analysis using real-life examples.
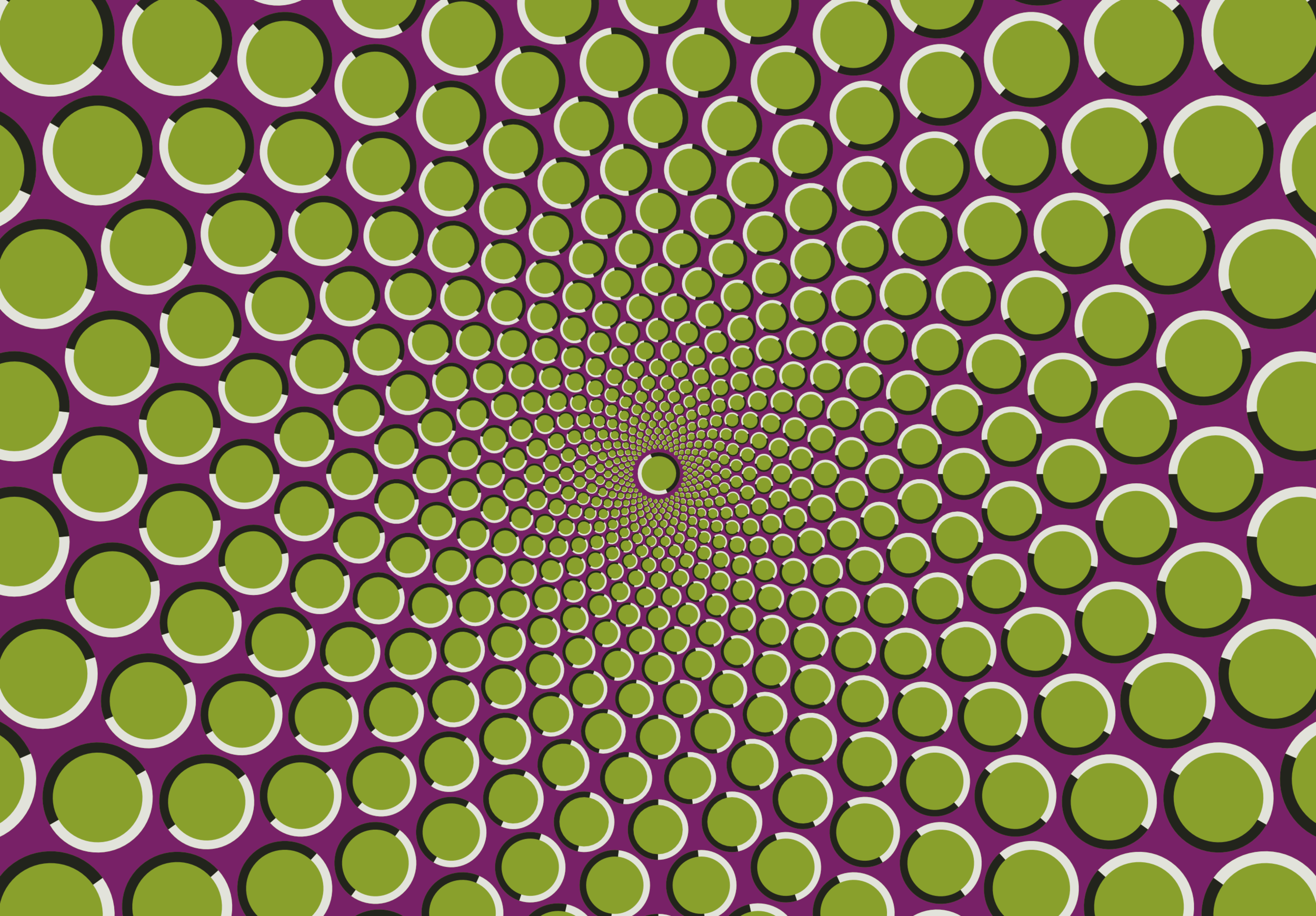
Sensory Neuroscience
Recommended audience: middle school and above
This lesson explores how our senses, such as vision and hearing, can get tricked using examples of illusions.
Virtual Exclusive
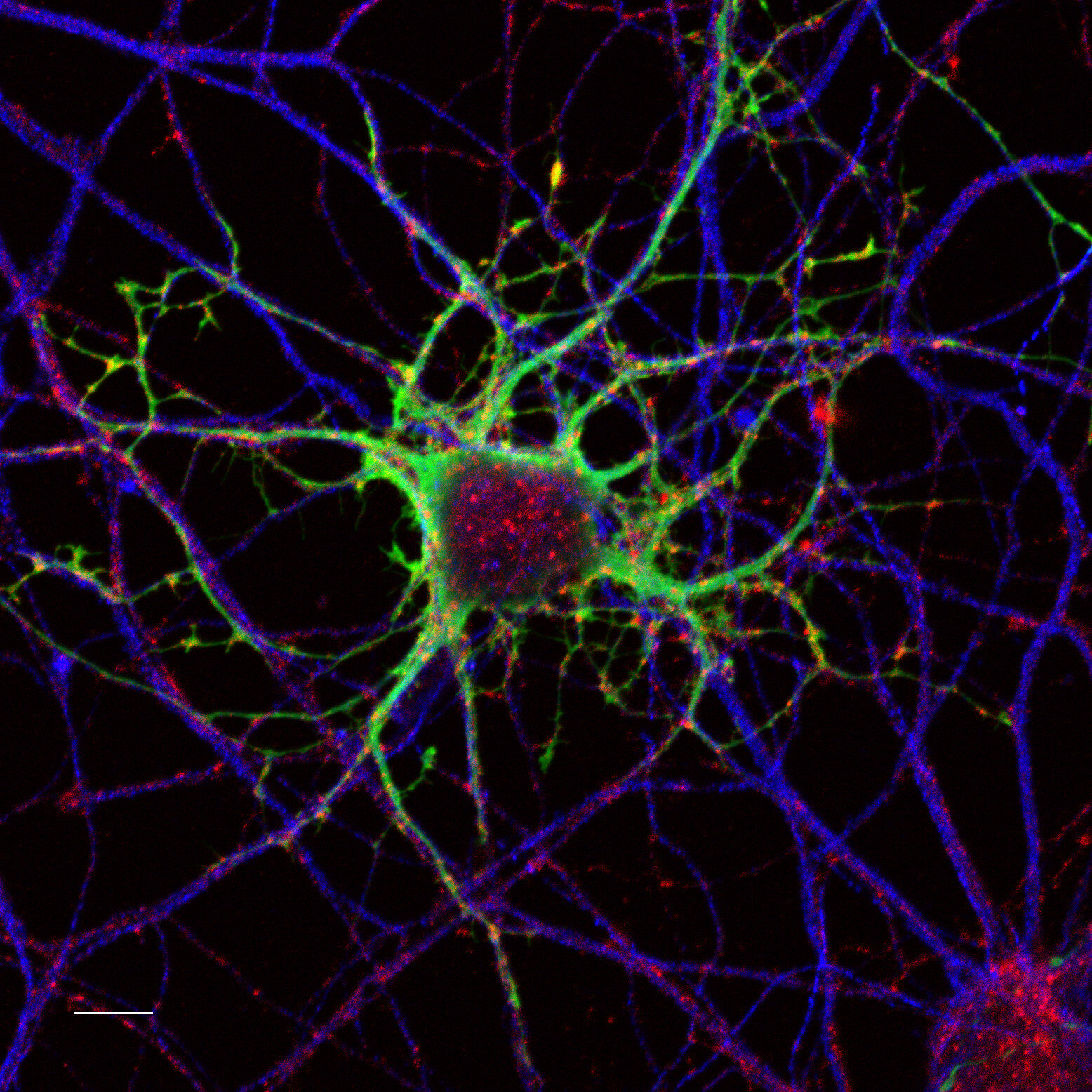
Imaging Methods
Recommended audience: middle school and above
An introduction into different methods and technologies scientists use to image the human brain and other biological samples.
In-Classroom Exclusive
Sheep Brains
Recommended audience: all ages and grades
A hands-on neuroanatomy lesson with real sheep brains.
Spiker Box
Recommended audience: all ages and grades
A lesson about how a neuron fires illustrated by "dancing" cockroach legs.
Building Neurons
Recommended audience: elementary school, grades K-5
This interactive lesson teaches the parts of a neuron and students will work together to build a giant 6-foot long neuron.
Prism Goggles
Recommended audience: all ages and grades
Students will participate in an experiment involving goggles, bean bags, and buckets, that demonstrates the visuo-motor plasticity of our brains.
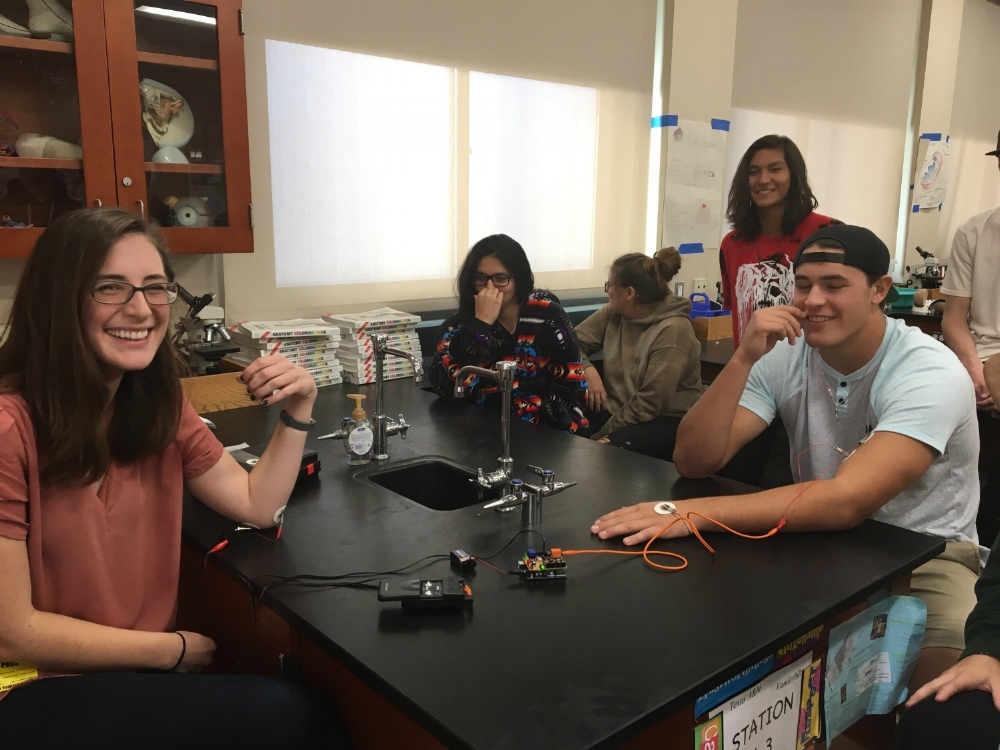
Electromyogram (EMG)
Recommended audience: all ages and grades
(Left) A 'shocking' lesson about the brain's ability to control muscles. (Below) A volunteer controls a robotic claw using signals from her muscles.